The Industrial Engineering Program
TABLE OF CONTENTS: (Click on a section to learn more)
The BSIE program consists of courses aimed to hone the critical thinking, analysis, and the overall personality of the student. There are four major areas of study, namely, Operations Research and Management Science, Production Systems, Information Systems, and Ergonomics or Human Factors Engineering. This program will produce professional Industrial Engineers equipped with the necessary technical and analytical skills and practical intelligence that will help them design, improve and install integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment, and energy, in whatever career path they will pursue.
Program Educational Objectives (PEO)
The BS Industrial Engineering Program aims to produce graduates who:
1. manage and lead public and private organizations in designing, implementing, and improving processes and systems
2. pursue entrepreneurial and technology-based innovation ventures
3. engage in lifelong learning through professional practice, research, and graduate studies
Program Learning Outcomes (PLO)
A graduate of the BS Industrial Engineering should have the following ability to:
Common to all programs
A. Articulate the latest developments in their specific field of practice.
B. Effectively communicate orally and in writing using both English and Filipino languages.
C. Work effectively and independently in multi-disciplinary and multicultural teams
D. Demonstrate professional, social and ethical responsibility, especially in practicing intellectual property rights and sustainable development.
E. Preserve and promote “Filipino historical and cultural heritage”.
Common to all engineering programs
F. Apply knowledge of mathematics and science to solve engineering problems.
G. Design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data.
H. Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability, in accordance with standards.
I. Recognize the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning.
J. Understand contemporary issues.
K. Use techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice.
L. Apply knowledge and understanding of engineering and management principles as a member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
Specific to BS Industrial Engineering (adapted from CHED Draft of PSG for BSIE).
M. Design, develop, implement, and improve integrated systems that include people, materials, information, equipment and energy.
N. Perform services in the form of analysis, design, and implementation of work standards, statistical process control systems, production plan and aterial control systems, manufacturing and service facilities, operations research models for production and operations, and information systems.
O. Contribute to nation building by engaging in research and other forms of creative work geared towards the improvement of the industrial engineering field.
Specific to the University of the Philippines
P. Lead with honor and excellence in public service and in fields of practice.
Curriculum Map
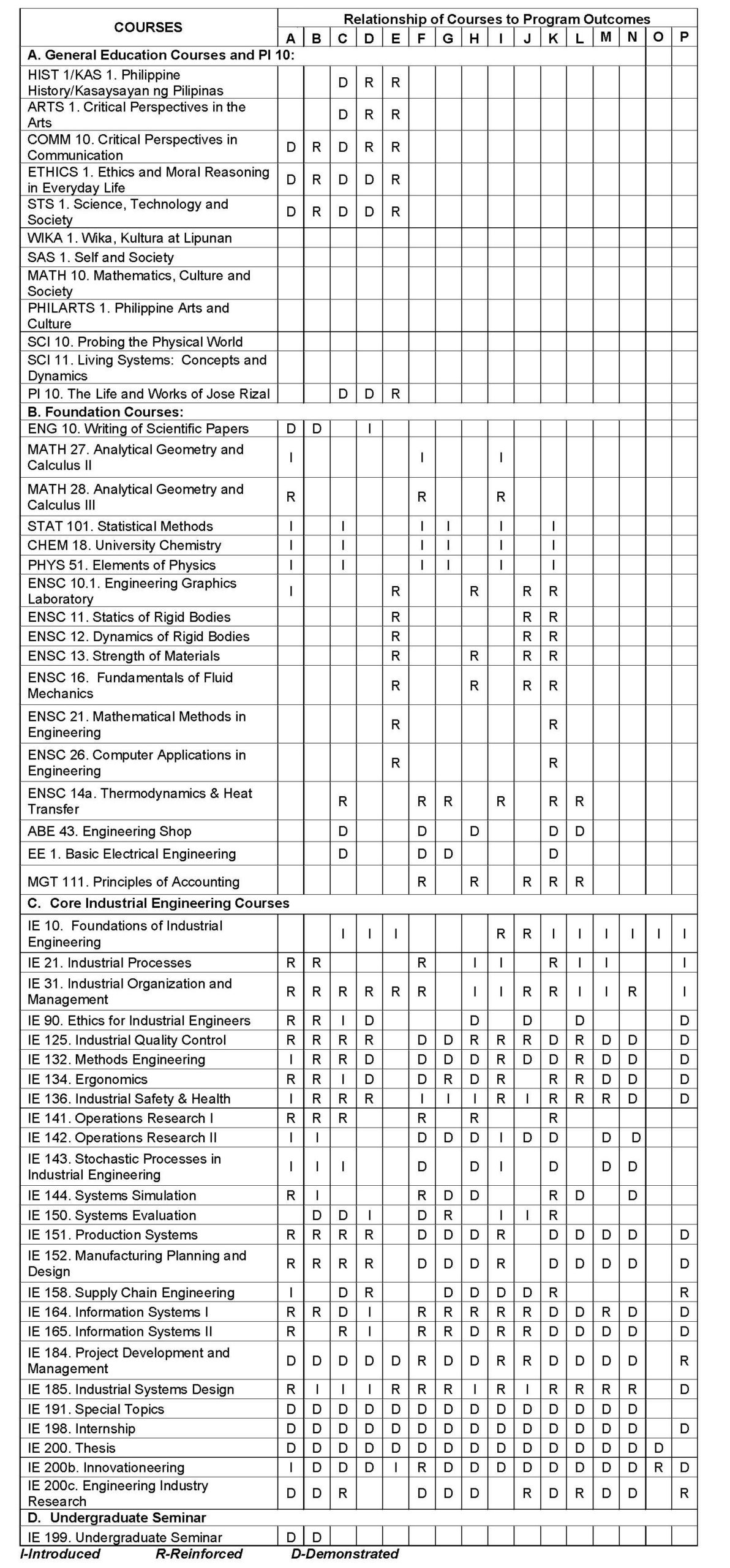
Courses Offered
Click on a course below for more information.
IE 3: Introduction to Industrial Engineering
Description: Systems concepts, the industrial organization and its functions; overview of industrial engineering tools.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): None
Offered during: 2nd Semester
IE 10: Foundations of Industrial Engineering
Description: Industrial engineering history development, perspective, and competencies.
Credit: 1 unit
Prerequisite(s): None
Offered during: 1st Semester
IE 21: Industrial Processes
Description: Industrial processes and their effects on production system decisions; metal, plastic, ceramic, elastomer, fiber, wood and pulp processes.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: PHYS 82, CHEM 15, and CHEM 15.1
- For 2018 Curriculum: PHYS 51 and CHEM 18
IE 31: Industrial Organization and Management
Description: Basic features governing the industrial organization; administration and financing of industries; relations between management and labor.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: IE 3
- For 2018 Curriculum: None
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 90: Ethics for Industrial Engineers
Description: Engineering code of ethics and relevant laws and regulations in industrial engineering practice.
Credit: 2 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 31
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 125: Industrial Quality Control
Description: Statistical process control charts; specifications and tolerances; acceptance sampling; reliability and life testing.
Credit: 5 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 21 and STAT 101
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 132: Methods Engineering
Description: Measurement, improvement, and design of work systems.
Credit: 5 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 21 and IE 31
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 134: Ergonomics
Description: Anthropometry; biomechanics; human task analysis; displays and control; work environments; ergonomic work design and evaluation.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 132
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 136: Industrial Safety and Health
Description: Accident prevention and reduction of health hazards in the work environment; control of noise, vibration and heat stress.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 134
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 141: Operations Research I
Description: Operations research methodology; recurrent processes and problems in industrial systems; optimization models for linear systems; linear programming, graph theory, and network analysis.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: ENSC 21
- For 2018 Curriculum: MATH 28
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 142: Operations Research II
Description: Other OR techniques such as advanced LP, ILP, goal programming, dynamic programming and game theory.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 141
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 143: Stochastic Processes in Industrial Engineering
Description: Analysis of different probabilistic models relevant for the industrial engineering profession.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): STAT 101
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 144: Systems Simulation
Description: Representation and simulation of systems; random number generation; record processing and generation of statistics.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 143 and IE 151
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 150: Systems Evaluation
Description: Criteria for evaluation of systems; technological economic, and human factors.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: MATH 38
- For 2018 Curriculum: MATH 28
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 151: Production Systems
Description: Planning, implementing and managing production operations within the system.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: IE 125, IE 141, and IE 150
- For 2018 Curriculum: IE 125, IE 132, and IE 141
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 152: Production Planning and Design
Description: Location and layout of facilities; materials handling, storage and distribution.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: IE 151
- For 2018 Curriculum: IE 150 and IE 151
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 158: Supply Chain Engineering
Description: Concepts, processes and best practices used in design and improvement of supply chains of goods and services.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 152 or COI (must have taken production management courses)
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 164: Information Systems I
Description: Analysis and design of information systems.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: CMSC 11
- For 2018 Curriculum: ENSC 26
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 165: Information Systems II
Description: Implementation considerations in information systems design; relational database systems.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: COI
- For 2018 Curriculum: IE 164
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 184: Project Development and Management
Description: Phases of project feasibility studies; project development, evaluation and management.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s)
- For 2014 Curriculum: IE 151
- For 2018 Curriculum:
- For BSIE students: IE 152
- For BSCE students: COI – Junior Standing (78 units), FPPS 183, and CE 132
- For BSEE students: COI – FPPS 183 and EE 60/EE 61/EE 65 (depending on the specialization)
IE 185: Industrial Systems Design
Description: Total systems design; integration of subsystem with concentration on optimal total systems implementation.
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): IE 184
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 190: Special Problems
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): COI
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
IE 191: Special Topics
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: COI (earned 159 units)
- For 2018 Curriculum: COI (IE 184 and earned 121 units)
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
IE 198: Internship
Credit: 3 units
Prerequisite(s): COI
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
IE 199: Undergraduate Seminar
Credit: 1 unit
Prerequisite(s):
- For 2014 Curriculum: COI (earned 159 units)
- For 2018 Curriculum: COI (currently taking IE 200/200b/200c)
Offered during: 1st and 2nd Semesters
IE 200: Undergraduate Thesis
Credit: 6 units
Prerequisite(s): COI
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
IE 200b: Innovationeering
Credit: 6 units
Prerequisite(s): COI
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
IE 200c: Engineering Industry Research
Credit: 6 units
Prerequisite(s): COI
Offered during: 1st Semester, 2nd Semester, and Midyear
GE Elective Courses
MATH 10: Mathematics, Culture and Society
PHILARTS 1: Philippine Arts and Culture
SAS 1: Self and Society
SCIENCE 10: Probing the Physical World
SCIENCE 11: Living Systems: Concepts and Dynamics
WIKA 1: Wika, Kultura at Lipunan
SOSC 3: Exploring Gender and Sexuality
HUM 3: Reading Film, TV and the Internet
PHLO 1: Philosophical Analysis
Technical Cognates
IE 191: Special Topics
CHE 180: Agro-Industrial Waste Management
MGT 131: Organizational Behavior
MGT 133: Personnel Management
CMSC 21: Fundamentals of Programming *
CMSC 22: Object-Oriented Programming *
